字符串String
一个字符的序列使用成对的单引号或双引号括起来或者三引号""" 和 ''' 表示块注释
字符串运算
长度 len()函数
first_name = 'Michael'len(first_name)>>>7
拼接 +
name = first_name + 'Jordan'print name>>>Michael Jordan
重复 *
name * 3>>>'Michael Jordan Michael Jordan Michael Jordan'
必须乘整数、只能字符串
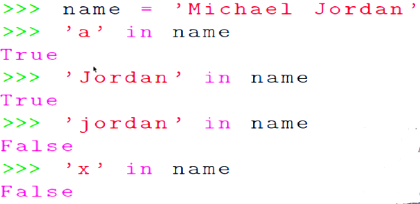
成员运算符 in
判断一个字符串是否是另一个字符串的子串返回值:True 或者 False
for 语句
枚举字符串的每个字符

计算一个字符串中元音字母的个数
def vowles_count(s): count = 0 for c in s: if c in 'aeiou': count += 1 return countprint vowles_count('Hello world') 字符串索引 index
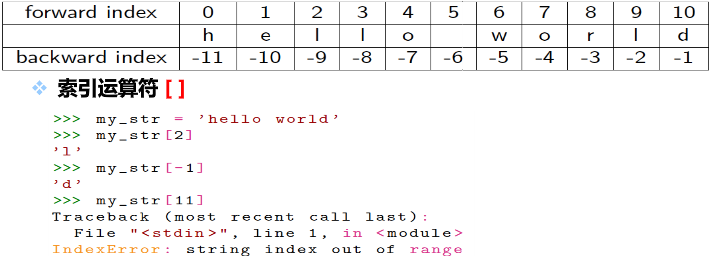
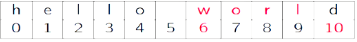
+字符串中每个字符都已一个索引值,也叫下标
+索引从0(前向)或-1(后向)开始[ ]
切片 Slicing
+选择字符串的子序列
语法 [start : finish]
start: 子序列开始位置的索引值finish: 子序列结束位置的下一个字符的索引值
如果不提供start或者finish,默认start为第一个字符开始,finish为最后一个字符
计数参数 Count by Argument
+接收三个参数
[start : finish : countBy] 默认countBy为1my_str = 'hello world'my_str[0:11:2]>>>'hlowrd'
+获得逆字符串
-1my_str = 'spam'reverse_str = my_str[::-1]print reverse_str>>>maps
字符串是不可变的 Immutable
+一旦生成,则内容不能改变

+通过切片等操作,生成一个新的字符串

字符串方法 Methods
+方法
+对象提供的函数
+注意
+replace 方法返回一个新的字符串,原字符串内容不变 +新字符串重新赋值给原来的变量更多字符串方法
find

split

其他方法
dir(str) ...人名游戏
人名列表文件names.txt,将每个人名转换为首字母大写,其他字母小写的格式
line不仅包括本行内容,还包括回车,输出本行内容后,还输出回车
.strip() 去掉字符串开始和结尾的空格、回车等
.title() 字符串变成首字母大写,其余字母小写
f = open('names.txt','r')for line in f: line = line.strip() print line.title() f.close () 编写一个名为is_palindrome的函数判断一个人名是否为回文,入“BOB”
f = open('names.txt','r')
def is_palindrome(name):
low = 0 high = len(name) - 1while low < high: if name[low] != name[high]: return False low += 1 high -= 1 return True
for line in f:
line = line.strip() if is_palindrome(line): print linef.close ()
2.递归实现
f = open('names.txt','r')def is_palindrome_rec(name): if len(name) <= 1: return True else: if name[0] != name[-1]: return False else: return is_palindrome_rec(name[1:-1])for line in f: line = line.strip() if is_palindrome_rec(line): print linef.close () 字符串比较
+任何一个字符都对应一个数字
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) +直接比较对应数字的大小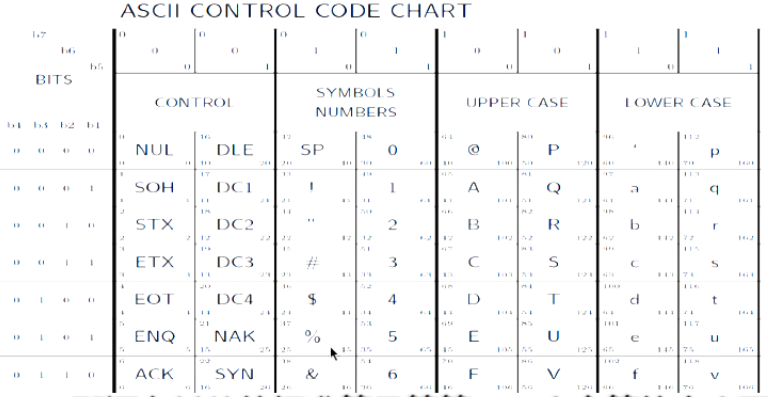
字典序 Dictionary order
+首先比较两个字符串的第一个字符
+如果相同,则比较下一个字符 +如果不同,则字符串的大小关系由这两个字符的关系决定 +如果其中一个字符为空(较短),则其更小
编写函数 is_ascending,判断一个人名的字母是否为升序排列(允许重复字母)
f = open('names.txt','r')def is_ascending(name): p = name[0] for c in name: if p > c: return False p = c return True for line in f: line = line.strip() if is_ascending(line): print linef.close () 字符串格式化 Formatting
+输出更规格的结果
format方法,如:
+括号的格式
{field name:align width.precision type} 域名:对齐方式 整数-占用宽度.精度 类型对齐方式:> 向右对齐,< 向左对齐

正则表达式 Regular Expressions
+判断一个人名(name)是否满足下列模式

c?a ?表示任意一个字符
c?a *表示任意多个字符+正则表达式 用来描述字符串的模式
.表示任意字符 \d+ 表示一系列数字 [a-z]表示一个小写字母 ....判断一个人名是否含有C.A模式
import ref = open('names.txt','r')for line in f: line = line.strip() pattern - 'C.A' result = re.search(pattern,line) if result: print 'Name is {}'.format(line) f.close() 正则表达式非常强大